- Published on
Hands-on Flink
- Authors

- Name
- Brian
- @gameofby
1. Getting Started
1.1. 概述
- 有状态。状态本地存储,异步定时异地备份
1.2. 环境
http://localhost:8081/ 本机的dashboard
2. Try Flink
2.1. Fraud Detection with the DataStream API
V0
V1 & V2
package org.apache.flink.api.common.functions; import org.apache.flink.annotation.Public; import org.apache.flink.configuration.Configuration; import java.io.Serializable; /** * An abstract stub implementation for rich user-defined functions. Rich functions have additional * methods for initialization ({@link #open(Configuration)}) and teardown ({@link #close()}), as * well as access to their runtime execution context via {@link #getRuntimeContext()}. */ // stub methods:类似占位mock、placeholder,用户可以丰富逻辑 @Public public abstract class AbstractRichFunction implements RichFunction, Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; // -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- // Runtime context access // -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- // RuntimeContext是个interface,有实际的StreamingRuntimeContext等实现。详见: private transient RuntimeContext runtimeContext; @Override public void setRuntimeContext(RuntimeContext t) { this.runtimeContext = t; } @Override public RuntimeContext getRuntimeContext() { if (this.runtimeContext != null) { return this.runtimeContext; } else { throw new IllegalStateException("The runtime context has not been initialized."); } } @Override public IterationRuntimeContext getIterationRuntimeContext() { if (this.runtimeContext == null) { throw new IllegalStateException("The runtime context has not been initialized."); } else if (this.runtimeContext instanceof IterationRuntimeContext) { return (IterationRuntimeContext) this.runtimeContext; } else { throw new IllegalStateException("This stub is not part of an iteration step function."); } } // -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- // Default life cycle methods // -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- @Override public void open(Configuration parameters) throws Exception {} @Override public void close() throws Exception {} }- 判断为欺诈交易的条件:前置交易为小额(<1),紧接着大额交易(>500),并且间隔小于1分钟
- 实现:使用ValueState记录每个账户的状态(flag, timer);在变更的时间节点维护好变更
- 为啥要用ValueState?
- 自动实现了针对每个Key上下文(这个例子中是account id)的状态保存
- flink提供的原生ValueState,实现了容错机制,可以从错误中重启恢复
How to build and run scala maven project in vscode?
- Metals,vscode里的scala插件,支持智能编辑、compile、build、执行等。详见:https://github.com/scalameta/metals-vscode。 官网(好多图墙了打不开):https://scalameta.org/metals/docs/editors/vscode/
- Bloop:Metals的build、debugger集成插件。在sbt、maven等build工具上又加了一层,大一统。详见:https://scalacenter.github.io/bloop/
- Maven
- scope:maven按照scope打包不同范围的依赖。详见:dependency mechanism
- WorkSheets
Todo:
- flink系统在代码层面,如何实现的分布式容错ValueState?RuntimeContext是在哪里set的实际的上下文
2.2. Real Time Reporting with the Table API
环境
- 如何vscode开发、打包、测试、运行java project?参考。放弃了,各种兼容问题,转IDEA
Table API
Apache Flink offers a Table API as a unified, relational API for batch and stream processing, i.e., queries are executed with the same semantics on unbounded, real-time streams or bounded, batch data sets and produce the same results. The Table API in Flink is commonly used to ease the definition of data analytics, data pipelining, and ETL applications
- 提供了batch和streaming一致的语义。可以batch数据(构造test数据集)上做测试,然后部署在streaming环境
- 类似于spark的DataFrame API,有各种 built-in functions,可以对Table进行各种SQL式变换。built-in functions如果不能满足,也可以写UDF
Windows:用来聚合时间。是flink的自带函数。相比于floor或者udf实现的group,运行时可以添加很多优化。
Todo
- 入门docker
- 把任务运行起来
2.3. Flink Operations Playground
结合docker,运维整个flink环境。
todo:待实践3. Learn Flink
3.1. Overview
training聚焦于这些点:continuous processing of streaming data, event time, stateful stream processing, and state snapshots
- Streaming Processing:介绍了下流处理批处理区别
- Parallel Dataflows:强调并行、分布式,和spark没啥不同
- Timely Stream Processing:同样的代码,重复执行可以保证一致性;
- Stateful Stream Processing:state一般都分实例本地保存在KV store。
- Fault Tolerance via State Snapshots:定期异步对state做快照
3.2. Intro to the DataStream API
a example for DataStream API
todo:hands-on3.3. Data Pipelines & ETL
Overall
- One very common use case for Apache Flink is to implement ETL (extract, transform, load) pipelines that take data from one or more sources, perform some transformations and/or enrichments, and then store the results somewhere
Stateless Transformations
- map()
- flatMap():1 -> n。n可以等于0,等价于过滤
Keyed Streams
- keyBy():key可以是实时计算出来的。计算必须保证确定性,实现hashCode(), equals()函数,不可以是随机数或者array、enum。因为同一个key可能被重复计算,多次计算的结果需要一致
Aggregations on Keyed Streams
- maxBy:关注一点,流处理过程中,聚合函数的结果是仅限于当前已经计算过的input。maxBy只是当截止前最大,不是整体最大
- (Implicit) State:这里flink隐含实现了state来记录截止当前每个key的最大值
- reduce
- maxBy:关注一点,流处理过程中,聚合函数的结果是仅限于当前已经计算过的input。maxBy只是当截止前最大,不是整体最大
Stateful Transformations
- Why is Flink Involved in Managing State?
- Using RichFunction implements Keyed State
- keyed state的实现是隐式的,代码里看不到记录每个key state的map
- Clearing State:无限的流式输入,需要清理过期的state。因为state的存储不是无限的
Connected Streams
- 多个stream输出源。 可以一个控制另一个,也可以实现join
- 处理多个stream的方法,默认是无法控制先后顺序的,取决于输入源的先后和flink处理的先后
- 如果想要强制控制处理顺序,需要引入state或者flink的其他能力
3.4. Streaming Analytics
3.4.1. Event Time and Watermarks
Introduction
Working with Event Time
Watermarks
- reorder the input stream by event time。event实际到达的时间可能是乱序的,需要缓存、延迟等待,才能尽可能确保t(event time)之前的event都到达了
- 但是也不能无止境的等下去,因为前置的event可能delay很久
- watermarks登场了,插入stream的断言来表明t之前的数据都到达了(大概率)
- 生成watermarks的算法可以有很多种。设置对伐delay时间的简单算法,已经表现得足够好
Latency vs. Completeness
- 从另一个角度理解watermarks。在latency and completeness之间权衡。
- 也可以混合两种策略,先快速产生结果,然后更新那些late event
Lateness
- 超过watermarks t时间的,都是late event
Working with Watermarks
- using WatermarkStrategy
3.4.2. Windows
Introduction
- to compute aggregated analytics
- Window Assigners:assign events to windows (creating new window objects as necessary)
- Window Functions:applied to the events assigned to a window
Window Assigners
- 介绍了一些flink built-in assigners
Window Functions
三种可选的处理windows中数据的方式
as a batch,using a
ProcessWindowFunctionas a stream, 增量实时处理。using
ReduceFunctionor anAggregateFunction结合1、2。
给出了1、3的代码例子
Late Events
- 默认是drop掉
- 可以用sideoutput把late event单独收集输出
- 也可以延长lateness设置,默认是0。延长后,在延长范围内的event还是会被收集
Surprises
- 一些被大家问了很多的共性问题回答
3.5. Event-driven Applications
加入timer。没细看,应该和一开始的fraud detection例子差不多
3.6. Fault Tolerance
这篇都是精华,值得细看。主要讲Flink容错机制的细节,以及Exactly-once语义的细节
https://ci.apache.org/projects/flink/flink-docs-release-1.13/docs/learn-flink/fault_tolerance/
4. Concepts
4.1. Overview
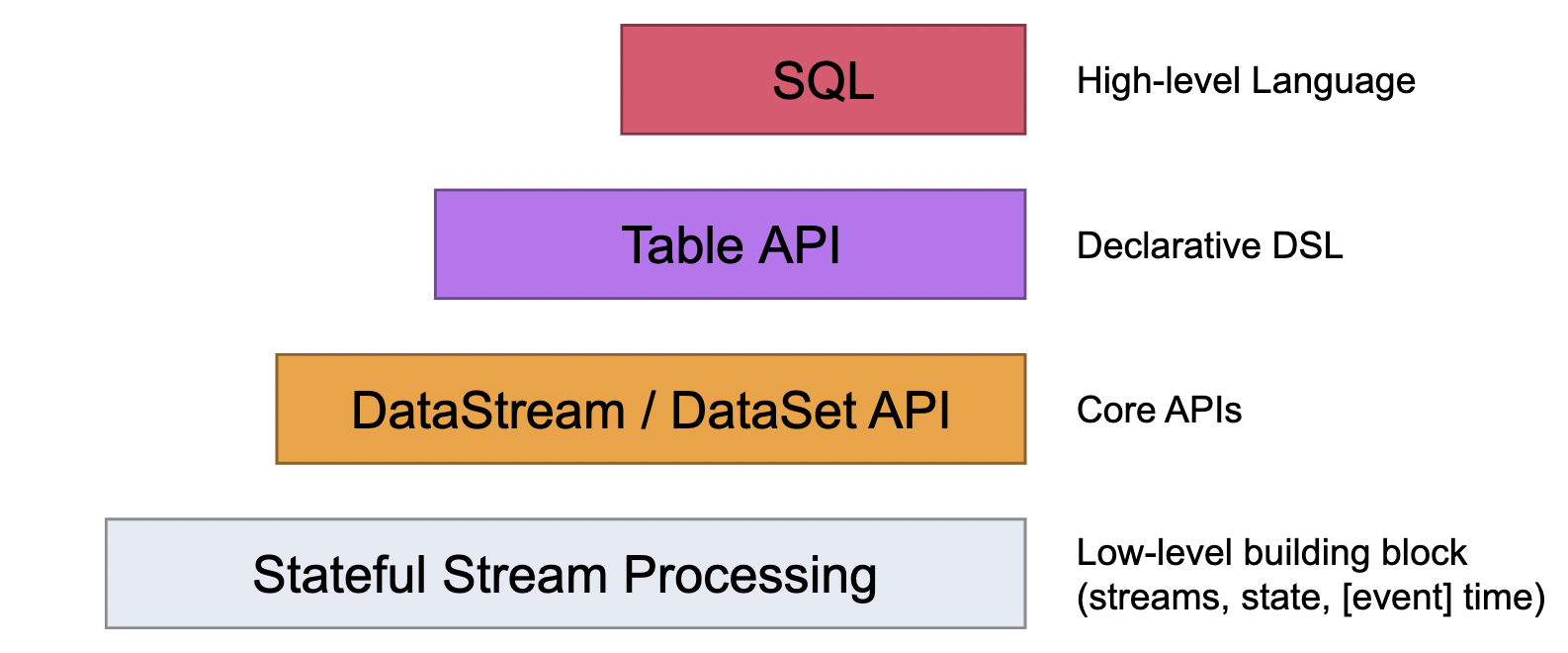
可以和spark类比来理解。SQL类似spark sql,Table API类似DataFrame API。DataStream/DataSet API不知道是否和rdd类似,待确认
4.2. Flink Architecture
值得精读: https://nightlies.apache.org/flink/flink-docs-release-1.13/docs/concepts/flink-architecture/